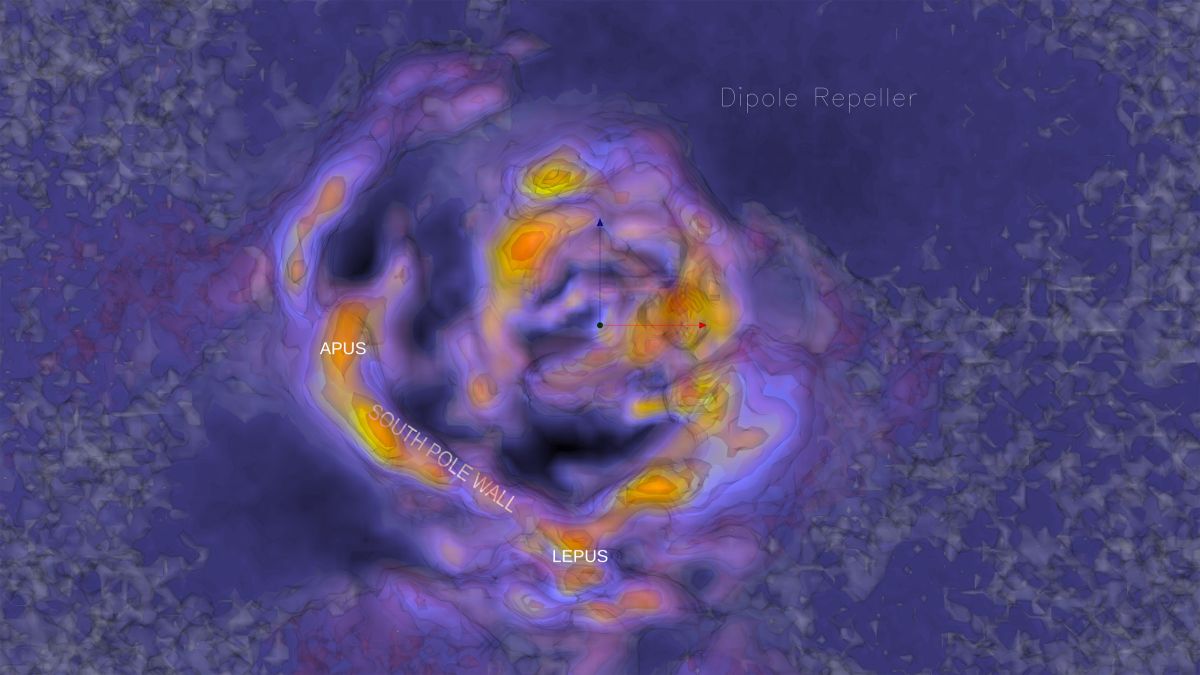
Amazing 3D maps of the universe have uncovered just one of the most important cosmic constructions ever observed — an almost-inconceivable wall stretching 1.4 billion mild-decades across that has hundreds of hundreds of galaxies.
The South Pole Wall, as it is really been dubbed, has been hiding in basic sight, remaining undetected until now due to the fact big pieces of it sit 50 % a billion light-yrs away driving the vibrant Milky Way galaxy. The South Pole Wall rivals in dimensions the Sloan Good Wall, the sixth most significant cosmic construction identified. (1 gentle-calendar year is around 6 trillion miles, or 9 trillion kilometers, so this “largest cosmic structure” is thoughts-bendingly humongous.)
Astronomers have long found that galaxies are not scattered randomly during the universe but instead clump jointly in what’s identified as the cosmic web, monumental strands of hydrogen gasoline in which galaxies are strung like pearls on a necklace that encompass gigantic and largely vacant voids.
Linked: Cosmic report holders: The biggest objects in the universe
Mapping these intergalactic threads belongs to the field of cosmography, which is “the cartography of the cosmos,” review researcher Daniel Pomarede, a cosmographer at Paris-Saclay College in France, explained to Reside Science.
Earlier cosmographic work has charted the extent of other galactic assemblies, such as the existing structural file holder, the Hercules-Corona Borealis Excellent Wall, which spans 10 billion mild-yrs, or additional than a tenth the dimension of the visible universe.
In 2014, Pomarede and his colleagues unveiled the Laniakea supercluster, a galactic collection in which our own Milky Way resides. Lanaikea is 520 million light-weight-a long time broad and has about the mass of 100 million billion suns.
For their new map, the staff applied freshly-made sky surveys to peer into a area referred to as the Zone of Galactic Obscuration. This is an location in the southern section of the sky in which the brilliant mild of the Milky Way blocks out a great deal of what’s driving and around it.
Cosmographers commonly establish the distance to objects utilizing redshift, the pace at which an object is receding from Earth because of to the expansion of the universe, which is dependent on their length, Pomarede reported. The farther absent an item is, the a lot quicker it will look to be receding from Earth, an observation initially created by astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1929 and which has held up at any time because.
But he and his colleagues utilized a marginally unique strategy, hunting at the peculiar velocity of galaxies. This measurement features redshift but also can take into account the motion of galaxies about 1 an additional as they tug at every other gravitationally, Pomarede mentioned.
The gain of the method is that it can detect hidden mass that is gravitationally influencing how galaxies shift and therefore uncover dim subject, that invisible things that emits no light but exerts a gravitational tug on something around ample. (Dim issue also tends to make up the bulk of the make any difference in the universe.) By running algorithms searching at peculiar movement in galactic catalogs, the team was equipped to plot the 3-dimensional distribution of matter in and all over the Zone of Galactic Obscuration. Their findings are in-depth today (July 9) in The Astrophysical Journal.
The resulting map demonstrates a head-boggling bubble of content extra or less centered on the southernmost point of the sky, with a terrific sweeping wing extending north on 1 side in the course of the constellation Cetus and one more stubbier arm reverse it in the route of the constellation Apus.
Related: The 12 strangest objects in the universe
Figuring out how the universe appears to be on this kind of substantial scales can help ensure our present-day cosmological products, Neta Bahcall, an astrophysicist at Princeton University in New Jersey who was not involved in the operate, informed Live Science. But identifying wherever exactly these huge, crisscrossing constructions start and end is challenging, she added.
“When you glimpse at the network of filaments and voids, it results in being a semantic issue of what’s related,” she claimed.
In their paper, the team acknowledges that they may not have plotted nevertheless the entirety of the broad South Pole Wall. “We will not be specific of its complete extent, nor no matter whether it is strange, till we map the universe on a appreciably grander scale,” they wrote.
Initially revealed on Dwell Science.

Devoted music ninja. Zombie practitioner. Pop culture aficionado. Webaholic. Communicator. Internet nerd. Certified alcohol maven. Tv buff.