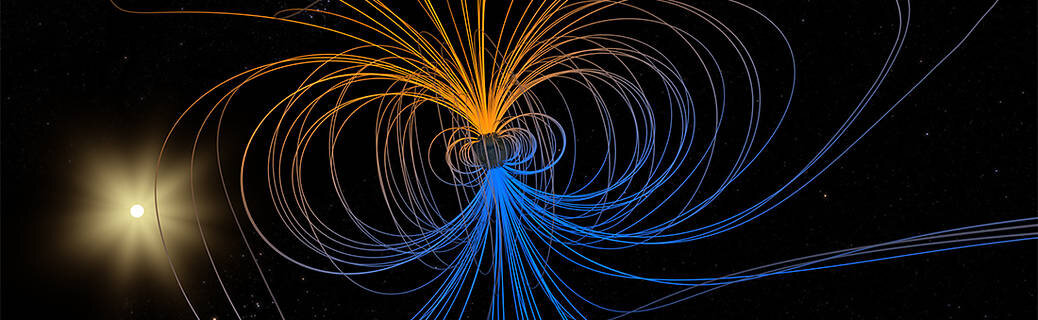
A little but evolving dent in Earth’s magnetic area can trigger major complications for satellites.
Earth’s magnetic discipline functions like a protecting protect all around the earth, repelling and trapping charged particles from the Sun. But over South The united states and the southern Atlantic Ocean, an unusually weak place in the field—called the South Atlantic Anomaly, or SAA—allows these particles to dip nearer to the area than ordinary. Particle radiation in this region can knock out onboard computer systems and interfere with the info selection of satellites that pass by means of it—a vital rationale why NASA researchers want to track and research the anomaly.
The South Atlantic Anomaly is also of interest to NASA’s Earth scientists who keep track of the alterations in magnetic subject energy there, both of those for how such variations have an affect on Earth’s atmosphere and as an indicator of what’s happening to Earth’s magnetic fields, deep within the globe.
At this time, the SAA makes no noticeable impacts on daily lifetime on the floor. Nevertheless, the latest observations and forecasts show that the region is growing westward and continuing to weaken in depth. It is also splitting—recent facts shows the anomaly’s valley, or location of minimum amount industry energy, has break up into two lobes, creating added difficulties for satellite missions.
A host of NASA experts in geomagnetic, geophysics, and heliophysics investigation groups observe and design the SAA, to observe and predict long run changes—and support get ready for future worries to satellites and people in area.
It truly is what is actually inside of that counts
The South Atlantic Anomaly arises from two features of Earth’s main: The tilt of its magnetic axis, and the movement of molten metals in its outer main.
Earth is a little bit like a bar magnet, with north and south poles that stand for opposing magnetic polarities and invisible magnetic field traces encircling the earth concerning them. But not like a bar magnet, the main magnetic industry is not correctly aligned by means of the world, nor is it completely secure. That is since the industry originates from Earth’s outer main: molten, iron-loaded and in vigorous motion 1800 miles underneath the surface. These churning metals act like a substantial generator, called the geodynamo, creating electric currents that produce the magnetic industry.
https://www.youtube.com/view?v=qpdQcw_52iM
As the main motion variations above time, due to complicated geodynamic conditions in the core and at the boundary with the reliable mantle up previously mentioned, the magnetic discipline fluctuates in area and time as well. These dynamical processes in the core ripple outward to the magnetic field surrounding the world, generating the SAA and other attributes in the around-Earth environment—including the tilt and drift of the magnetic poles, which are relocating about time. These evolutions in the industry, which take place on a identical time scale to the convection of metals in the outer main, supply experts with new clues to help them unravel the main dynamics that drive the geodynamo.
“The magnetic industry is basically a superposition of fields from numerous present-day sources,” explained Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Centre in Greenbelt, Maryland. Areas exterior of the strong Earth also lead to the noticed magnetic field. Having said that, he mentioned, the bulk of the industry will come from the main.
The forces in the main and the tilt of the magnetic axis together deliver the anomaly, the location of weaker magnetism—allowing billed particles trapped in Earth’s magnetic field to dip closer to the surface.
The Solar expels a regular outflow of particles and magnetic fields recognised as the solar wind and wide clouds of scorching plasma and radiation termed coronal mass ejections. When this photo voltaic substance streams throughout space and strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, the house occupied by Earth’s magnetic field, it can become trapped and held in two donut-formed belts close to the earth called the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic subject lines, continually bouncing back again and forth from pole to pole. The innermost belt starts about 400 miles from the floor of Earth, which retains its particle radiation a healthy distance from Earth and its orbiting satellites.
On the other hand, when a specially potent storm of particles from the Sun reaches Earth, the Van Allen belts can become highly energized and the magnetic industry can be deformed, allowing for the charged particles to penetrate the environment.
“The observed SAA can be also interpreted as a consequence of weakening dominance of the dipole field in the area,” reported Weijia Kuang, a geophysicist and mathematician in Goddard’s Geodesy and Geophysics Laboratory. “Far more specifically, a localized field with reversed polarity grows strongly in the SAA region, therefore producing the area intensity incredibly weak, weaker than that of the surrounding areas.”
A pothole in place
Though the South Atlantic Anomaly occurs from processes inside of Earth, it has effects that achieve much beyond Earth’s surface. The area can be hazardous for very low-Earth orbit satellites that journey through it. If a satellite is hit by a higher-energy proton, it can limited-circuit and cause an function termed one occasion upset or SEU. This can trigger the satellite’s function to glitch briefly or can result in lasting hurt if a crucial ingredient is hit. In order to keep away from dropping devices or an entire satellite, operators frequently shut down non-important elements as they go through the SAA. In fact, NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer on a regular basis travels through the region and so the mission keeps consistent tabs on the SAA’s posture.

The Intercontinental Space Station, which is in minimal-Earth orbit, also passes by way of the SAA. It is very well protected, and astronauts are protected from harm when inside. On the other hand, the ISS has other passengers impacted by the greater radiation stages: Instruments like the World Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation mission, or GEDI, accumulate information from several positions on the outdoors of the ISS. The SAA results in “blips” on GEDI’s detectors and resets the instrument’s electric power boards about once a thirty day period, claimed Bryan Blair, the mission’s deputy principal investigator and instrument scientist, and a lidar instrument scientist at Goddard.
“These functions result in no harm to GEDI,” Blair mentioned. “The detector blips are scarce in comparison to the number of laser shots—about a single blip in a million shots—and the reset line celebration results in a few of hours of missing info, but it only comes about every month or so.”
In addition to measuring the SAA’s magnetic field toughness, NASA experts have also researched the particle radiation in the region with the Photo voltaic, Anomalous, and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer, or SAMPEX—the initially of NASA’s Small Explorer missions, launched in 1992 and supplying observations until 2012. One particular research, led by NASA heliophysicist Ashley Greeley as aspect of her doctoral thesis, employed two a long time of knowledge from SAMPEX to display that the SAA is slowly but surely but steadily drifting in a northwesterly course. The outcomes assisted verify designs produced from geomagnetic measurements and showed how the SAA’s locale alterations as the geomagnetic subject evolves.
“These particles are intimately associated with the magnetic industry, which guides their motions,” stated Shri Kanekal, a researcher in the Heliospheric Physics Laboratory at NASA Goddard. “For that reason, any information of particles presents you details on the geomagnetic industry as perfectly.”
Greeley’s success, printed in the journal Room Climate, were being also equipped to present a clear image of the form and quantity of particle radiation satellites get when passing via the SAA, which emphasized the want for continuing checking in the area.
The details Greeley and her collaborators garnered from SAMPEX’s in-situ measurements has also been handy for satellite structure. Engineers for the Lower-Earth Orbit, or LEO, satellite applied the effects to design and style programs that would reduce a latch-up function from producing failure or reduction of the spacecraft.
Modeling a safer upcoming for satellites
In purchase to recognize how the SAA is transforming and to put together for upcoming threats to satellites and instruments, Sabaka, Kuang and their colleagues use observations and physics to lead to global types of Earth’s magnetic industry.

The crew assesses the recent point out of the magnetic industry making use of facts from the European Room Agency’s Swarm constellation, previous missions from businesses all-around the world, and floor measurements. Sabaka’s workforce teases apart the observational data to separate out its resource in advance of passing it on to Kuang’s team. They blend the sorted information from Sabaka’s group with their core dynamics product to forecast geomagnetic secular variation (immediate adjustments in the magnetic area) into the potential.
The geodynamo versions are one of a kind in their capability to use main physics to create in the vicinity of-upcoming forecasts, claimed Andrew Tangborn, a mathematician in Goddard’s Planetary Geodynamics Laboratory.
“This is equivalent to how weather conditions forecasts are generated, but we are working with a lot extended time scales,” he mentioned. “This is the essential difference amongst what we do at Goddard and most other analysis teams modeling variations in Earth’s magnetic discipline.”
One these types of application that Sabaka and Kuang have contributed to is the Intercontinental Geomagnetic Reference Industry, or IGRF. Utilized for a selection of analysis from the main to the boundaries of the environment, the IGRF is a collection of applicant styles manufactured by around the world research groups that describe Earth’s magnetic area and monitor how it variations in time.
“Even even though the SAA is slow-moving, it is going through some change in morphology, so it really is also critical that we preserve observing it by obtaining ongoing missions,” Sabaka stated. “Due to the fact that’s what aids us make versions and predictions.”
The altering SAA offers scientists new options to understand Earth’s core, and how its dynamics impact other factors of the Earth method, explained Kuang. By tracking this slowly but surely evolving “dent” in the magnetic discipline, scientists can greater have an understanding of the way our world is transforming and aid get ready for a safer future for satellites.
Study reveals strange magnetic behaviour 8-11 million a long time ago
NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Centre
Citation:
NASA scientists monitor slowly and gradually splitting ‘dent’ in Earth’s magnetic subject (2020, August 17)
retrieved 17 August 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-08-nasa-track-gradually-dent-earth.html
This document is topic to copyright. Aside from any good working for the goal of private analyze or exploration, no
section may possibly be reproduced without the need of the penned permission. The material is offered for data reasons only.

Devoted music ninja. Zombie practitioner. Pop culture aficionado. Webaholic. Communicator. Internet nerd. Certified alcohol maven. Tv buff.